Overview
Lagrange's network can be thought as an indexer that looks at a contract's storage and process it into a verifiable database.
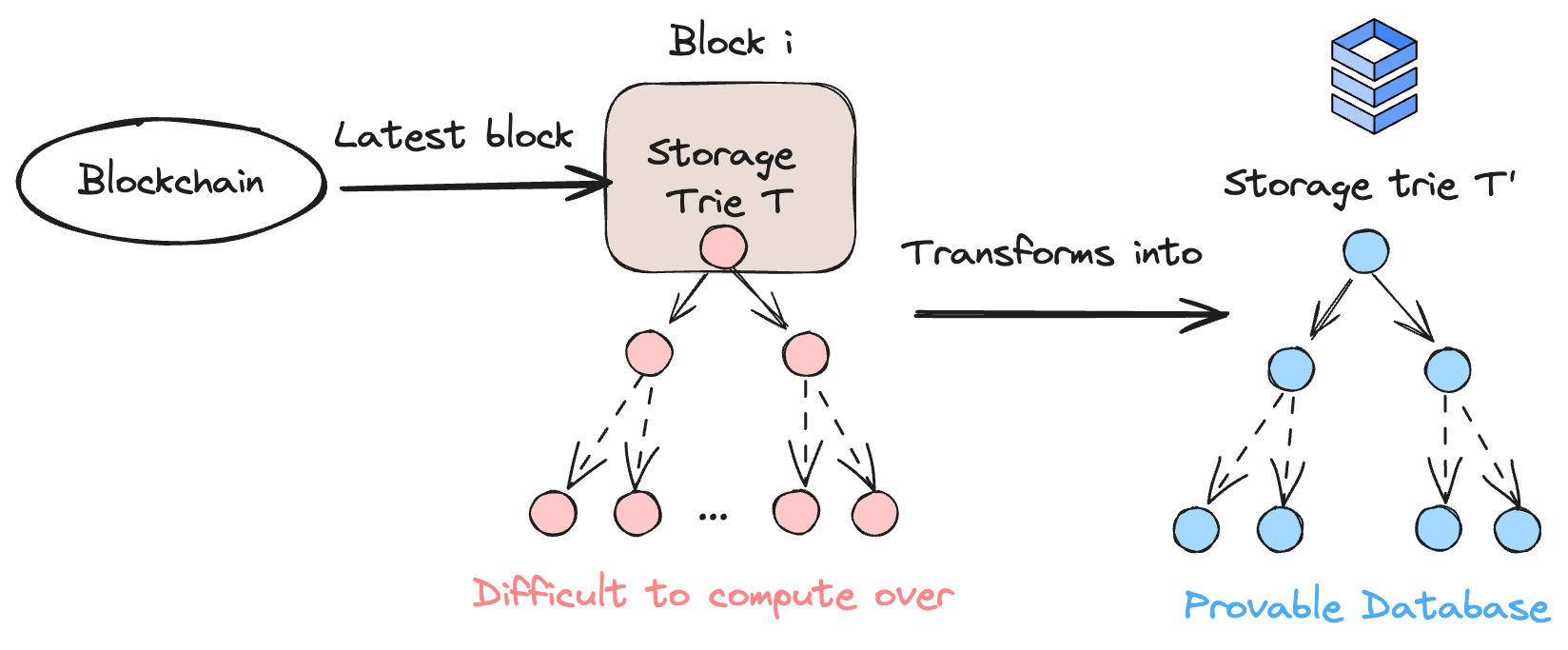
Lagrange's network is in essence, re-creating the target blockchain's database (storage, state and blocks) but in a format amenable to run efficient and distributed queries.
More precisely, the ZK Coprocessor is producing for each block a new equivalent version (in blue) of the original storage trie (in red), but which is supporting efficient queries. In the above diagram, we generate a proof that this new database contains the same data as the original red blockchain data structure.
Note: From this section onwards, the explanation is deeply technical and requires knowledge of data structures such as Merkle Patricia Trie.